Course Index:
Introduction: Software Development (SDLC)
|
Different
Methodologies - Software Development
|
Predictive Vs Adaptive Methodologies
|
Why Agile?
|
Agile Principles
|
Comparison between Different Agile Methods
|
Introduction to Scrum
|
Scrum Roles and Tasks
|
PM Vs Scrum Master
|
Scrum Events
|
Scrum Artifacts
|
Estimation in Scrum
|
Scrum Metrics
|
Scrum of Scrum
|
Responsibilities of PO and SM
|
Agile Disadvantages
|
Scrum Management Tools - Comparison
|
JIRA Board
|
Scrum Revision
|
Introduction:
Software Development (SDLC)
Different
Methodologies - Software Development
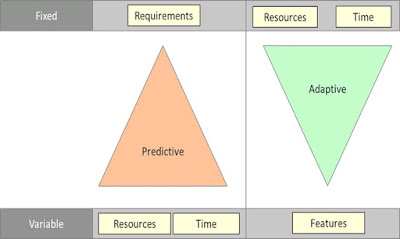
Predictive
Vs Adaptive Methodologies
Why Agile?
•
Change is Embraced
•
End-goal can be Unknown
•
Faster, high-Quality Delivery
•
Strong Team Interaction
•
Customers are Heard
•
Continuous Improvement
Agile Manifesto and Principles
- Manifesto
•
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
•
Working software over comprehensive documentation
•
Working
software is more useful and welcome than just presenting documents to clients
in meetings
•
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
•
Requirements
cannot be fully collected at the beginning of the software development cycle,
therefore continuous customer or stakeholder involvement is very important.
•
Responding to change over following a plan
•
Agile
methods are focused on quick responses to change and continuous development.
- Principles
•
Customer
satisfaction by early and continuous delivery of valuable software
•
Welcome
changing requirements, even in late development
•
Working
software is delivered frequently (weeks rather than months)
•
Close,
daily cooperation between business people and developers
•
Projects
are built around motivated individuals, who should be trusted
•
Face-to-face
conversation is the best form of communication (co-location)
•
Working
software is the principal measure of progress
•
Sustainable
development, able to maintain a constant pace
•
Continuous
attention to technical excellence and good design
•
Simplicity—the
art of maximizing the amount of work not done—is essential
•
Best
architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams
Regularly, the team
reflects on how to become more effective, and adjusts accordingly
Comparison between different Agile methods
Characteristic
|
XP
|
Scrum
|
FDD
|
Crystal
|
Development Style
|
Iterative Increments
|
Iterative Increments
|
Iterative Increments
|
Iterative Increments
|
Project Team Size
|
Fewer than twenty people (small team)
|
All size
|
Large Team
|
All size
|
Team Distribution
|
Co-located
|
Co-located and Distributed team
|
Co-located and Distributed team
|
Co-located
|
Customer Involvement
|
Involved
|
Customer involvement through the role of product owner
|
Customer involved through reports
|
Customer involved through releases
|
Level of Documentation
|
Basic and as little as possible
|
Basic and anything of value
|
Vital
|
Basic documentation
|
Iteration Time Period
|
One to six weeks
|
Two to four weeks
|
Two days to two weeks
|
Depending on Crystal method
|
Introduction
to Scrum
Scrum Roles and Tasks
ROLE – Scrum Master
Ensures the project
team is working on the correct tasks and has everything needed to complete
their work
TASKS
•
Interacts
daily with the project team to ensure progress is made
•
Ensures
that the team’s established software development processes are followed
•
Ensures
each team member is assigned tasks
•
Removes
blocking issues so team members can accomplish their tasks
•
Coordinates
with the product owner to ensure requirements are available and prioritized
•
Coordinates
with the project manager to ensure the team’s progress is accurately
communicated
ROLE – Product Owner
Owns the vision and
requirements for the project, thus controlling what the team works on.
TASKS
•
Works
with external stakeholders to define overall project requirements
•
Documents
requirements and their priorities
•
Communicates
with the scrum master on the list of requirements and their priorities
•
Clarifies
requirement questions and expectations
ROLE - Analyst
Serves as the
conduit between the product owner and the project team so that everyone
understands each other
TASKS
•
Works
with the product owner to define requirements within the product’s environment,
budget and scope
•
Documents
business and system requirements
•
Translates
technical issues for product owner and external stakeholders
•
Provides
clarification on requirements for the project team
ROLE – QA Lead
Leads and provides
direction to the QA team.
TASKS
•
Provides
direction on the activities of the team.
•
Establishes
the testing processes for the entire team
•
Coordinates
with the scrum master to ensure the team is working on the correct items
•
Coordinates
with the product owner, analyst or design team to determine deviation from
requirements or as-designed feature
ROLE – QA Team
Tests the product to
ensure quality specifications are met.
TASKS
•
Creates
test cases
•
Tests
the product (manual or automated)
•
Logs
defects
ROLE – Design Lead
Leads and provides
direction to the design team
TASKS
•
Provides
design direction and vision for the project
•
Coordinates
with the scrum master to ensure the team is working on the correct items
ROLE – Design Team
Provides visual
design assets for the product.
TASKS
•
Creates
visuals that can be used to apply the proper design for the product
•
Creates
assets that will be used within the product
•
Provides
support to the dev / QA teams to ensure designs are followed
ROLE – Project manager
Keeps track of the
budget, schedule and scope
of the project and
communicates status to all
Stakeholders
TASKS
•
Works
with stakeholders to define budget, schedule and scope of the project
•
Ensures
the team is working toward its goals and remains on track for project delivery
•
Collects
status and communicates it with the entire team and stakeholders
•
Organizes
and drives meetings with the team and third parties to ensure all dependencies
are understood and met
•
Mitigates
issues that will impact the budget, schedule or scope of the project
ROLE – Dev Lead
Leads and provides
direction to the dev team
TASKS
•
Provides
direction on the architecture of the project (or works with the architecture
team), coding standards and what tasks each developer works on
•
Establishes
the development processes for the entire team
•
Coordinates
with the scrum master to ensure the team is on the right track.
ROLE – Dev Team
Develops the product
according to desired specifications.
TASKS
•
Implement
requirements and change requests
•
Fix
defects
Coordinate with the
product owner, analyst or design team for clarification on requirements
Project
Manager vs Scrum Master
Scrum
Events
Scrum
Artifacts
Estimation
in Scrum
Scrum
Metrics
Scrum
of Scrum
•
What has your team accomplished since our last meeting?
•
What problems occurred, if any, that negatively affected your team?
•
What does your team want to accomplish before we meet again?
•
What output from your team in future sprints, do you see as possibly
interfering with the work of other teams?
•
Does your team see any interference problems coming from the work of
other teams?
Responsibilities of PO and SM
Product Owner's Responsibilities
- Voice of
the Stakeholders, represents the business
- Manages
stakeholder relationships, communications & expectations
- Accountable
for the vision, scope and scale of the product
- Defines key
features of the product & success criteria
- Continuously
refines requirements
- Sets
delivery schedule by managing the backlog – creates and updates the
release plan, including prioritization
- Accountable
for the project success
- Decides on
release date, content and budget
- Accepts and
rejects work in the sprint reviews
- Takes
advice from the team on Backlog Dependencies
- Single
point of contact for the product (including New requirements Prioritizing
backlog items)
Scrum Master's Responsibilities
- Responsible
for helping the team deliver work to the Product Owner
- Makes sure
the team can meet its commitments by removing any impediments they face,
including Managing dependencies, escalating blockers that they cannot
remove themselves
- Facilitates
process & meetings (e.g. Reviews, Stand Ups, Planning, Estimation,
Scheduling, Prioritization)
- Makes sure
the team is fully functional, productive and improving quality
- Shields the
team from distractions and interferences (including the Product Owner)
- Enables
close co-operation across all roles and functions, removes barriers
- Responsible
for reporting progress, including producing standard outward-facing
artefacts
Agile Disadvantages
•
Disadvantages
•
Relatively New
•
People are afraid of what they do not know
•
People tend to know what they are getting
upfront before they commit budget
•
Difficult to scale for large projects where
Documentation is essential
•
Needs experience and skill if not to degenerate
into
•
code-and-fix
•
If not managed well, the execution can be too
Agile
Scrum Management Tools – Comparison
Scrum
Revision













No comments:
Post a Comment